B (Bulb) Setting:- A shutter-speed setting on an adjustable camera that allows for time exposures. When set on B, the shutter will stay open as long as the shutter release button remains depressed. Another similar option is the "T" setting, where it never drains the battery power on automatic camera body.
Background:- The part of the scene that appears behind the principal subject of the picture. The sharpness of the background can be influenced by apertures and shuttle set. In the flash mode, bulb setting usually is set for absorbing more ambience light (background information), so the end result of the exposure won't be pitch dark.
Background density:- - density of any selection of a negative or print on which there is no image. Also referred to as Fog level.
Backing:- - dark coating, normally on the back of a film, but sometimes between emulsion and base, to reduce halation. The backing dye disappears during processing.
Backlighting:- Light coming from behind the subject, toward the camera lens, so that the subject stands out vividly against the background. Sometimes produces a silhouette effect. Always use something (a hand, a lens shade to avoid the light falls onto the lens - to avoid lens flares).Light coming from behind the subject, toward the camera lens, so that the subject stands out vividly against the background. Sometimes produces a silhouette effect.
Back-Printing:- Information printed on the back of a picture by the photofinisher. The system standard requires the printing of frame number, film cassette number and processing date automatically on the back of each Advanced Photo System print; may also include more detailed information, such as customized titles and time and date of picture- taking.
Bag bellows:- - short flexible sleeve used on large format cameras in place of normal bellows when short focal length lenses are employed.
Barrel Distortion:- Straight lines are bowed in at the edges of the picture frame re sembling the sides of a barrel; pres ent in small amounts in some wideangle or wideangle-zoom lenses, bu~ uncorrected in fisheye lenses.
Balance:- Placement of colors, light and dark masses, or large and small objects in a picture to create harmony and equilibrium. Description applied to colour films to indicate their ability to produce acceptable colour response in various types of lighting. The films normally available are balanced for daylight (550~6000K photo lamps (3400K) or studio lamps (3200K).
Balanced Fill-Flash:- : A type of TTL auto flash operation which uses the camera's exposure meter to control ambient light exposure settings, integrated with flash exposure control. That is, flash output level is automatically compensated to balance with ambient light, resulting in a better exposure for both subject and background.
Balanced fill-flash operation:- : A flash photography technique that balances flash illumination with the scene's ambient light. This automatic operation utilizes the some camera's Automatic Balanced Fill Flash System with TTL Multi Sensor and a compatible dedicated TTL Speedlight.
Barium sulfate:- - compound used in the manufacture of photographic printing paper to give bright white highlights in the final print.
Barn doors: - accessory used on spotlights and flood lamps to control the direction of light and width of the beam.
Barrel distortion:- - one of the common lens aberrations, where straight lines at the edge of the field are caused to bend into the shape of a barrel.
Baryta:- - coating of barium sulfate applied as the foundation to fiber based printing papers.
Base:- - support for photographic emulsions. Available in a choice of materials, including paper, cellulose, triacetate, glass and estar.
Baseboard camera:- - portable large format camera with a folding base-board. Allows a limited use of camera movements. Also referred to as a field camera.
Base Exposure Time:- - initial exposure time used for making a "straight" print.
Base-relief:- - photographic image effect usually produced by printing from a negative and a positive sandwiched together in the enlarger, slightly out of register.
Batch numbers:- - set of numbers printed on packages of sensitive materials to indicate common production coating.
Beam splitter:- - mirror and prism system capable of partly reflecting, partly transmitting light.
Belitski's reducer:- - solution used as a chemical reducer for negatives. It consists of ferric potassium citrate or oxalate in an acid fixing solution.
Bellows:- The folding (accordion) portion in some cameras that connects the lens to the camera body (like the Mamiya RZ). Also a camera accessory that, when inserted between lens and camera body, extends the lens-to-film distance for close focusing or macro phtography. Some retains the automatic functions where some have to stopdown the lens for manual exposure reading.
Between-The-Lens Shutter:- A shutter whose blades operate between two elements of the lens. Most medium format cameras like the Hasselblad have one family of lens with shuttle and another without. Most lenses in this family have a smaller maximum aperture than the other family.
Bichromate:- - refers to potassium bichromate or potassium dichromate, used for bleaching and as a sensitizer for gelatin.
Bi-concave lens:- - simple lens or lens shape within a compound lens, whose surfaces curve toward the optical center. Such a lens causes light rays to diverge.
Bi-convex lens:- - simple lens shape whose surfaces curve outward, away from the optical center. Such a lens causes light rays to converge.
Binocular vision:- - visual ability to determine three dimensions. Stereoscopic photography depends on the use of binocular vision.
Bi-pack:- - combination of two films, differently sensitized, but exposed as one.
Bi-refringence:- - splitting of light passing through certain kinds of crystals into two rays at polarized right angles to each other.
Bispheric lens:- - lens having different curvatures at the center and the edge, each of which forms part of a sphere. The different edge curvature brings the peripheral rays more closely to the same point of focus as the center rays.
Bitumen:- - hydro-carbon which hardens by the action of light. It was used by Joseph Nicephore Niepce to produce the worlds first photograph in the early 19th century.
Black silver:- - finely divided metallic silver formed from silver halides by exposure and development.
Bleach:- - chemical bath capable of rehalogenizing black metallic silver.
Bleaching:- - stage in most toning, reducing and color processing systems.
Bleach-out:- - method of producing line drawings from photographic images. The photographic is processed in the normal way, its outlines sketched, and the black metallic silver image is then bleached away to leave a drawn outline.
Bleed:- - term used to describe a picture with no borders, which has been printed to the edge of the paper.
Blocked up:- - a portion of an overexposed and/or overdeveloped negative so dense with silver halides that texture and detail in the subject are unclear.
Blocking out:- - method of painting selected areas of a negative with an opaque liquid on the non-emulsion side. Since light is unable to penetrate these areas they appear white on the final print.
Blotter:- - sheet or sheets of absorbent material made expressly for photographic prints. Wet prints dry flat and quickly when placed between blotters.
Blowup:- An enlargement; a print that is made larger than the negative or slide.
Blue print:- - alternative term for cyanotype.
Blue sensitive:- - sensitive to blue light only. All silver halides used in traditional black and white emulsions are sensitive to blue light, but early photographic materials had only this sensitivity.
Blur:- - unsharp image areas, created or caused by subject or camera movement, or by selective or inaccurate focusing.
Boom:- - adjustable metal arm, attached to a firm stand, on which lighting can be mounted. Some booms are also made to support cameras.
Borax:- - mild alkali used in fine grain developing solutions to speed up the action of the solution.
Border:- - edge of a photographic print - either left white, or printed black.
Boric acid:- - compound used in certain fixers to prolong shier hardening life.
Bounce Lighting:- Flash or tungsten light bounced off a reflector (such as the ceiling or walls) or attachment that fits on the flash (like the LumiQuest's Pocket Bouncer) to give the effect of natural or available light.
Box camera:- - simplest type of camera manufactured, and first introduced by George Eastman in 1888. It consists of a simple, single element lens, a light tight box and a place for film in the back.
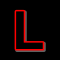
Bracket flash:- Often called handle mount flash. It comprised of one arm of the L-shaped bracket extends under the camera body and uses the camera's tripod socket to mount the camera on the bracket. The vertical arm of the bracket serves as a handle and mounts a flash unit in an accessory shoe often on top of the handle portion, but there are other methods. Flash mounted in a bracket usually requires a separate electrical cord to make the electrical connection between camera body and flash unit.
Brightfield:- - method of illumination used in photomicrography which will show a specimen against a white or light background.
Brightline viewfinder:- - viewfinder in which the subject is outlined by a bright frame, apparently suspended in space. This may show parallax correction marks, or lines indicating the fields of view of different focal lengths.
Brightness range:- - subjective term describing the difference in illumination between the darkest and lightest areas of the subject.
Brilliance:- - intensity of light reflected from a surface. It is sometimes an alternative term for luminosity.
Broad lighting:- - portrait lighting in which the main light source illuminates the side of the face closes to the camera.
Brometching:- - obsolete, special method of producing a bromide print. The result acquired the texture of its support and appeared similar to an etching.
Bromide paper:- - most common type of photographic printing paper. It is coated with an emulsion of silver bromide to reproduce black & white images.
Bromoil process:- - old printing process invented in 1907, consisting of three stages. First, an enlargement is made on bromide paper and processed. Second, the silver image is removed in a bleacher which also modifies the gelatin so it will accept lithographic ink. Third, while still damp the gelatin is inked up by hand to create the image.
Brownie:- - trade name given to early Kodak box cameras.
Brush development:- - method of development in which developer is applied to the material with a brush or similar instrument.
BSI:- - abbreviation for British Standards Institute.
Bubble chamber photography:- - method of analyzing the paths of high-speed sub-atomic particles.
Buffer:- - chemical substance used to maintain the alkalinity of a developing solution, particularly in the presence of bromine which is produced during development.
Built-in meter:- - reflective light meter built directly into the camera so that exposures can be easily made for the cameras position.
Bulb:- - See B below.
Bulk film:- - film purchased in long lengths. Used in a bulk camera back or with a bulk film loader.
Bracketing:- Taking a series of photographs of the same subject at different exposures to insure the "correct" exposure; useful when shooting in situations where a normal metering reading is difficult to obtain. Taking additional pictures of the subject through a range of exposures-both lighter and darker-when unsure of the correct exposure.Some top cameras have provision for automatic bracketing, while manually you can bracket by the use of, say, adjust apertures or shuttle speeds setting or both, manually influent the ASA setting or even adjust the flash output power etc..
Burning-In:- Basically, a darkroom process that gives additional exposure to part of the image projected on an enlarger easel to make that area of the print darker. This is accomplished after the basic exposure by extending the exposure time to allow additional image-forming light to strike the areas in the print you want to darken while holding back the image-forming light from the rest of the image. Sometimes called printing-in.
Bulb Flashbulbs:- A special flashbulb that can be used at certain shutter speeds is called "FP" where the initials stand for Focal Plane. Designed for use with focal-plane shutters these bulbs make a nearly uniform amount of light for a relatively long time. The idea is to turn on the light before the focal-plane shutter starts to open and keep the light on until the shutter is completely closed. Firing delay for flashbulbs is indicated by code letters: "F"- fast; "M"- medium; "MF" - mediurn fast; "S" - slow